What are the Surge Protectors?
A surge protector, also known as a surge suppressor or transient voltage suppressor (TVS), is a special electrical device designed to protect electronic and electrical equipment from voltage spikes, transient overvoltage, and surges in electrical power systems. has been done These surges can originate from a variety of sources, including lightning strikes, power grid disruptions, or the sudden switching on and off of high-power electrical equipment.

Main Components and Mechanisms
Voltage Clamping: The primary function of a surge protector is to limit the voltage that reaches the connected devices. This is achieved by components such as metal oxide transistors (MOVs) or avalanche diodes. These components exhibit a nonlinear response to voltage, effectively “clamping” or diverting excess voltage away from the connected equipment.
Response time: Surge protectors are engineered to respond quickly to voltage spikes. Reaction time is important, as a fast reaction helps deflect the surge before it reaches and can potentially damage connected equipment. High-quality surge protectors have short response times, measured in nanoseconds.
Joule Rating: The Joule rating of a surge protector indicates its ability to absorb and dissipate energy from transient waves. A higher joule rating indicates a greater ability to handle multiple and larger surges before compromising its protective capabilities.
Clamping Voltage: The clamping voltage means the level at which the surge protector diverts excessive voltage. A lower clamping voltage indicates better protection, as it ensures that connected devices experience less surge voltage during surges.
Thermal fuses and safety features: Surge protectors often include safety features such as thermal fuses, which disconnect the surge protection components if they overheat due to prolonged exposure to surges. This helps prevent the surge protector itself from becoming a fire hazard.
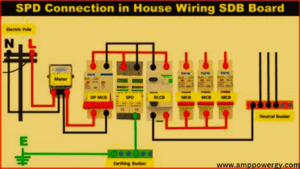
Application of Surge Protector
Surge protectors find applications in various settings where protection of electronic and electrical equipment from voltage surges is important. Here are some common applications:
Residential Use:Surge protectors are commonly used in homes to protect electronic devices such as computers, televisions, gaming consoles and audio systems from voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations.
Office Equipment: Surge protectors are deployed to protect computers, printers, scanners and other office electronics from possible damage due to power surges. They are often integrated into power strips for convenience.
Control systems: In industrial settings, surge protectors are used to protect control systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and other sensitive equipment from voltage spikes, ensuring reliable operation of manufacturing processes. goes
Networking equipment: Surge protection is important for protecting telecommunication infrastructure, routers, switches, modems and other networking equipment from electrical surges in power or communication lines.
Medical Equipment: Hospitals and healthcare facilities use surge protectors to protect sensitive medical equipment, including diagnostic imaging machines, patient monitoring equipment and computer systems, from potential damage.
Server Rooms: Surge protectors play an important role in data centers to protect servers, storage systems, and networking infrastructure. Uninterruptible power is essential to maintain reliability and availability of data center operations.
Computer labs and classrooms: Surge protectors are commonly used in educational settings to protect computers and electronic devices in computer labs and classrooms, where multiple devices are connected to electrical outlets.
Point-of-sale systems: Retail establishments use surge protectors to protect point-of-sale (POS) systems, cash registers and electronic payment processing equipment from potential damage from power surges.
Home Theater: Surge protectors are essential components in home entertainment systems, protecting expensive audio-visual equipment, gaming consoles, and streaming devices from voltage surges.
Sensitive equipment: In research laboratories and scientific facilities, surge protectors are used to protect sensitive equipment and instruments, such as spectroscopy instruments and precision measuring instruments, from electrical disturbances.
Communication infrastructure: Surge protection is important to protect communication equipment, antennas and signal processing units from voltage fluctuations in the power supply or communication lines in telecom base stations.
surge protectors are widely used in various fields and settings to ensure the protection and reliable operation of electronic and electrical equipment when faced with unexpected voltage surges.
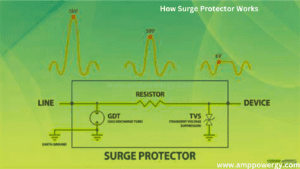
Working of Surge Protector
The operation of a surge protector involves several important components and mechanisms that collectively act to deflect, absorb and limit overvoltage during surges. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how a surge protector works:
Voltage Detection:
Surge protectors constantly monitor incoming electrical voltage. Under normal operating conditions, the voltage remains within a standard range. However, during the surge, the voltage increases significantly.
Voltage Clamping:
Surge protectors are voltage clamping devices, usually equipped with metal oxide resistors (MOVs) or avalanche diodes. These components show a non-linear response to voltage changes. When the voltage exceeds a certain threshold (clamping voltage), the resistance of these components drops dramatically.
Excess voltage absorption:
As the voltage exceeds the clamping voltage, the MOV or avalanche diodes within the surge protector become conductive, providing a low-impedance path for excess energy. This allows the surge protector to absorb and redirect overvoltage from connected devices.
Energy loss:
The surge protector dissipates the absorbed energy as heat. The duration of the surge and the energy absorption capacity of the surge protector determine how effectively it can handle transient overvoltage.
Response time:
Surge protectors operate with extremely fast response times, typically in the order of nanoseconds. This fast response ensures that excess voltage is suppressed before it reaches and potentially damages connected electronic equipment.
Joule Rating:
A surge protector is assigned a joule rating, which indicates its ability to handle the energy from a surge. A higher Joule rating means the surge protector can absorb more energy before compromising its protective capabilities.
Thermal Protection:
To prevent the surge protector from becoming a fire hazard itself, many devices incorporate thermal protection features. Thermal fuses or other mechanisms disconnect surge protection components if they become too hot due to prolonged exposure to surges.
Indicator lights:
Some surge protectors include indicator lights to signal their operational status. For example, a light can indicate whether a surge protector is still providing protection or if it needs replacement after absorbing several surges.
It is important to note that surge protectors have a limited lifespan and may wear out over time, especially if exposed to frequent surges. Consequently, periodic replacement of surge protectors is recommended to ensure continued effectiveness in providing protection for connected equipment. Additionally, the overall performance of a surge protector is affected by factors such as the quality of its components, clamping voltage, response time, and design.
Advantages of Surge Protectors
Device Protection: The primary benefit of surge protectors is that they help protect electronic and electrical equipment from potential damage caused by voltage surges. This includes sensitive devices such as computers, TVs, audio systems, and other electronics.
Cost-Effective Insurance: Surge protectors offer a cost-effective means of insurance for valuable and expensive electronic devices. Investing in a surge protector can save money by preventing the need for costly repairs or replacements of damaged equipment.
Data Integrity: For data storage devices, such as computers and external hard drives, surge protectors help maintain data integrity by preventing corruption or damage caused by voltage surges.
Fire Prevention: Surge protectors with safety features such as thermal fuses contribute to fire prevention by disconnecting surge protection components if they overheat due to prolonged exposure to surges.
Peace of mind: Knowing that connected devices are protected from unexpected voltage surges gives consumers peace of mind. This is especially important in areas with lightning activity or unstable power grids.
Extended Device Lifespan: Surge protectors play a role in extending the overall lifespan of electronic devices by preventing damage to internal components due to voltage surges.
Convenience: Surge protectors often come with multiple outlets, allowing users to connect multiple devices to a single protector. This not only reduces clutter but also makes it easy to centralize protection for all sensitive electronics.
Disadvantages of Surge Protectors
Limited lifespan: Surge protectors have a limited lifespan, and their effectiveness may decrease over time, especially after absorbing multiple surges. Periodic replacement is recommended to ensure continued protection.
Not fully comprehensive protection: Surge protectors primarily address voltage surges. They cannot protect against other power quality problems such as brownout or undervoltage. Additional measures, such as voltage regulators or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) may be required for comprehensive protection.
Not foolproof against lightning: Although surge protectors can reduce damage caused by lightning surges, they cannot provide complete protection against a direct lightning strike. Additional lightning protection measures may be required.
Quality Variability: The effectiveness of surge protectors can vary based on factors such as component quality, clamping voltage, and response time. Low-quality surge protectors may offer limited protection and reliability.
No protection for all devices: Surge protectors must be used correctly, and not all devices may be compatible. Some appliances, especially those with large power requirements such as air conditioners or appliances with motors, may not benefit significantly from surge protectors.
Over-reliance on aging protectors: Consumers may sometimes overestimate the longevity of surge protectors or fail to replace them after a long period of time. This can lead to a false sense of security and reduced security.
See Also:
Frequently asked question
Q: How often should I replace my surge protector?
Ans: Surge protectors have a limited lifespan, and it is generally recommended that they be replaced every 3 to 5 years, or sooner if they have been exposed to multiple surges. Regular replacement ensures continued effectiveness.
Q: Can I use a surge protector in conjunction with a power strip?
Ans: Yes, many surge protectors come in the form of power strips, which provide both additional outlets and surge protection. However, it is important to avoid overloading the circuit and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Q: Do surge protectors consume power while not in use?
Ans: Most surge protectors use a minimal amount of standby power, but this amount is usually negligible. Unplugging devices directly from the surge protector when not in use can further reduce any potential energy consumption.
Q: Can the surge protector be used outdoors?
Ans: Surge protectors designed for indoor use may not be suitable for outdoor applications. There are weather surge protectors designed specifically for outdoor use to protect equipment such as outdoor lighting or power tools.
Q: Do surge protectors protect against all types of electrical problems?
Ans: Surge protectors primarily address voltage surges, and although they provide some protection against power spikes and transients, they may not be effective against brownouts, undervoltage, or permanent overvoltage. Other devices such as voltage regulators or uninterruptible power supplies may be required for comprehensive protection.
Q: Can I be a daisy chain surge protector for more stores?
Ans: It is not generally recommended for daisy chain surge protectors. Doing so may create a risk of overloading the circuit and may compromise the effectiveness of the surge protection. Instead, consider using a surge protector with plenty of outlets.
Q: Do surge protectors come with a warranty?
Ans: Yes, many surge protectors come with a warranty provided by the manufacturer. Warranty periods and conditions may vary, so it is advised to check the product documentation for warranty information.
Q: Can a surge protector protect against lightning strikes?
Ans: Although surge protectors can provide some protection against surges caused by lightning, they cannot provide complete protection in the event of a direct lightning strike. Lightning protection systems and additional measures are recommended in areas with frequent lightning activity.
Q: Can I plug a refrigerator or air conditioner into a surge protector?
Ans: Large appliances with motors, such as refrigerators or air conditioners, can draw significant power during startup, and surge protectors may not provide enough protection. It is advisable to check the manufacturer’s instructions, and for such devices, a dedicated circuit may be a better solution.
Q: Can surge protectors be used in conjunction with generators?
Ans: Yes, surge protectors can be used with generators to protect electronic equipment from possible voltage surges during power transmission. However, it is important to ensure compatibility and follow proper installation practices.
Q: Do all surge protectors have the same level of protection?
Ans: No, surge protectors can vary in terms of quality, features and protection capabilities. Factors such as clamping voltage, response time, and Joule rating determine the level of protection a surge protector offers. Surge protectors must be selected based on the specific needs of the connected equipment.

1 thought on “What are the Surge Protectors?”