What is a DC Power Supply?
Definition:
A DC power supply, or direct current power supply, is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) from a power source into a steady, direct current (DC) output. It typically consists of components such as transformers, rectifiers, filters, and voltage regulators to convert and stabilize the input AC voltage into the desired DC voltage and current levels.
DC power supplies are widely used in various electronic devices and systems where a stable and regulated source of DC power is required, such as in electronics testing, telecommunications, computing, and industrial applications.

Working of DC power Supply
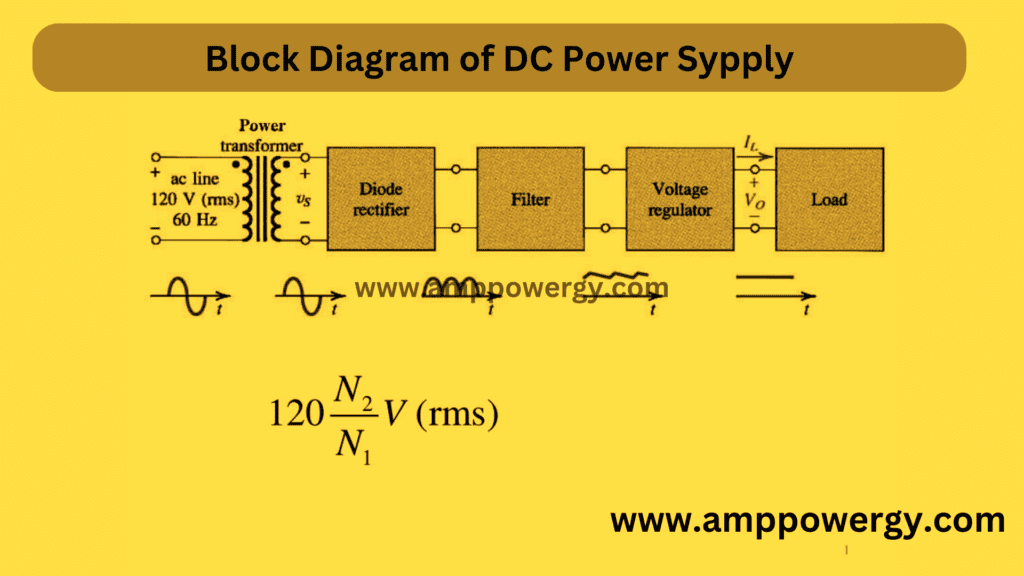
The working principle of a DC power supply involves several stages:
- Step-down Transformer: The incoming alternating current (AC) from the main power source is first passed through a step-down transformer. This transformer reduces the voltage level to a suitable range for further processing.
- Rectification: After the transformer, the AC voltage is converted into pulsating DC voltage using diodes. Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, effectively converting the negative half cycles of the AC waveform into positive. This process is known as rectification.
- Smoothing: The pulsating DC output from the rectifier contains ripples, which are undesirable fluctuations in voltage. To smooth out these ripples, a filter capacitor is used. The capacitor stores charge during the peaks of the pulsating waveform and releases it during the troughs, resulting in a smoother DC output.
- Regulation: The smoothed DC voltage still might not be at the desired level due to variations in load or input voltage. To ensure a stable output voltage regardless of changes in load or input, a voltage regulator circuit is employed. This circuit adjusts the output voltage by varying its resistance, maintaining a constant output voltage.
- Output: The regulated DC voltage is then provided as the output of the DC power supply, which can be used to power electronic devices or circuits.
Application of DC power Supply
DC power supplies find applications in various fields due to their ability to provide stable and regulated DC voltage. Some common applications include:
- Electronics Testing and Development: DC power supplies are extensively used in laboratories and manufacturing facilities for testing and prototyping electronic circuits and components. Engineers and technicians use them to provide precise and adjustable DC voltage to power their designs and analyze their performance.
- Telecommunications: DC power supplies are essential in telecommunications infrastructure, such as mobile base stations, communication satellites, and data centers. They provide the necessary power for operating communication equipment, ensuring uninterrupted communication services.
- Computing: DC power supplies are used in computing systems, including desktop computers, servers, and networking equipment. They provide stable DC power to various components such as processors, memory modules, and storage devices, ensuring reliable operation.
- Industrial Automation: In industrial automation and control systems, DC power supplies are used to power sensors, actuators, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), and other control devices. They provide the required voltage levels for precise control and monitoring of industrial processes.
- Medical Devices: DC power supplies are employed in various medical devices and equipment, including diagnostic instruments, imaging systems, and life support systems. They provide safe and regulated power for critical medical applications, ensuring patient safety and reliable operation.
- Renewable Energy Systems: DC power supplies play a crucial role in renewable energy systems such as solar power and wind power installations. They convert the DC output from solar panels or wind turbines into usable DC power for charging batteries, powering inverters, and supplying electricity to the grid or off-grid applications.
- Aerospace and Defense: DC power supplies are used in aerospace and defense applications, including avionics systems, radar systems, and missile guidance systems. They provide reliable power for critical electronic components in aircraft, spacecraft, and military equipment.
- Automotive: In automotive applications, DC power supplies are used in vehicle electronics, onboard computers, electric vehicle charging stations, and battery management systems. They provide stable DC power for powering various vehicle systems and accessories.
Advantage of DC power Supply
- Stability: DC power supplies provide a stable and consistent output voltage, which is crucial for powering sensitive electronic devices and circuits. This stability ensures reliable operation and accurate measurements in various applications.
- Efficiency: Compared to AC power supplies, DC power supplies can be more efficient since there is no need for the conversion of AC to DC during operation. This efficiency can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs, especially in continuous-use applications.
- Control: DC power supplies typically offer precise control over output voltage and current levels. Users can adjust these parameters as needed for specific applications, making DC power supplies versatile and adaptable to different requirements.
- Compact Size: DC power supplies can be designed to be relatively compact and lightweight, making them suitable for portable or space-constrained applications such as field testing, mobile electronics, and battery-powered devices.
- Safety: DC power supplies are often considered safer than AC power supplies since they do not have the alternating voltage and frequency associated with AC power. This can reduce the risk of electric shock and make DC-powered devices safer to handle and operate.
Disadvantages of DC power supply
- Limited Transmission Distance: DC power cannot be transmitted over long distances without significant power loss. This limitation necessitates the use of AC power for long-distance transmission, which is then converted back to DC using rectifiers at the destination.
- Cost: Depending on the complexity and features, DC power supplies can be more expensive to design, manufacture, and maintain compared to simpler AC power supplies. High-quality components, such as voltage regulators and filtering circuits, contribute to the overall cost.
- Complexity of Conversion: In some cases, DC power supplies may require the conversion of AC to DC, especially when the primary power source is AC. This conversion process adds complexity and may introduce inefficiencies, particularly in low-quality or poorly designed power supplies.
- Electrolytic Capacitor Wear: The smoothing capacitors used in DC power supplies, especially electrolytic capacitors, can degrade over time due to factors such as temperature, voltage stress, and aging. This degradation can lead to reduced performance or failure of the power supply if not properly maintained or replaced.
- Compatibility: Some devices and equipment may require AC power or have specific voltage and frequency requirements that are not easily met by DC power supplies. In such cases, additional conversion or adaptation may be necessary, adding complexity and potential points of failure.
Read Also:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a DC power supply?
- A DC power supply is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) into a steady, direct current (DC) output. It is used to provide stable and regulated DC voltage for powering electronic devices and circuits.
- What are the main components of a DC power supply?
- The main components of a DC power supply typically include a step-down transformer, rectifier diodes, a smoothing capacitor, voltage regulators, and output terminals.
- What is the difference between a linear and a switching DC power supply?
- Linear DC power supplies use a linear regulator to regulate the output voltage, while switching DC power supplies use a switching regulator. Switching power supplies are generally more efficient and lighter but may introduce more electrical noise.
- What are the applications of DC power supplies?
- DC power supplies are used in various fields, including electronics testing and development, telecommunications, computing, industrial automation, medical devices, renewable energy systems, aerospace, automotive, and more.
- How do I choose the right DC power supply for my application?
- Factors to consider when choosing a DC power supply include the required output voltage and current levels, regulation and stability requirements, efficiency, size and weight constraints, safety features, and budget.
- What is meant by voltage regulation in a DC power supply?
- Voltage regulation refers to the ability of a DC power supply to maintain a constant output voltage despite changes in input voltage or load conditions. Good voltage regulation ensures stable and reliable operation of connected devices.
- How do I troubleshoot problems with a DC power supply?
- Common troubleshooting steps include checking input power, verifying output voltage and current levels, inspecting connections and cables for damage, and testing components such as fuses and capacitors.
- Can a DC power supply be used to charge batteries?
- Yes, DC power supplies can be used to charge batteries by providing the appropriate voltage and current levels required for charging. However, it is essential to use a charging method suitable for the type of battery being charged to avoid overcharging or damage.
- Are there safety precautions I should take when using a DC power supply?
- Yes, safety precautions include following manufacturer’s instructions, using proper insulation and protective gear, avoiding contact with live components, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Where can I buy DC power supplies?
- DC power supplies are available from electronics retailers, online marketplaces, industrial suppliers, and specialized manufacturers. It’s essential to choose a reputable supplier and verify the specifications and quality of the product before purchase.
