What is a Motion Controller?
A motion controller is a device or system that manages and interprets the movement of objects or elements in a particular system. It usually includes sensors to detect motion and a processing unit to analyze and respond to that motion. In the context of gaming or virtual reality, a motion controller is often a handheld device that allows users to interact with a digital environment by translating their physical movements into action within a virtual space.
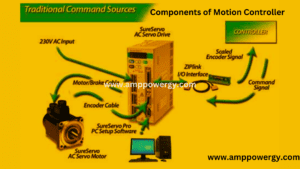
Components of Motion Controller
The components of a motion controller can vary depending on the specific application, but here are some common elements:
- Sensors: Motion controllers use various sensors to detect motion. These sensors can include accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers, and sometimes cameras or infrared sensors.
- Processing Unit: A dedicated processing unit or microcontroller analyzes the data from the sensors. It interprets motion signals and translates them into commands or actions for connected systems.
- Communication Interface: Motion controllers often have a communication interface to connect to the device or system they are controlling. This can include wired connections such as USB or wireless connections such as Bluetooth.
- Power Supply: Motion controllers require a power source to function. It can be powered by batteries or a wired power connection.
- Button or touch controls: In addition to motion sensing, many controllers have buttons, triggers, or touch-sensitive areas to allow users to input specific commands.
- Haptic Feedback: Some advanced motion controllers include a haptic feedback mechanism. These mechanisms provide tactile sensations to users, enhancing the immersive experience by simulating touch or force feedback.
These components work together to enable the motion controller to accurately capture and interpret body movements, providing a responsive and interactive experience in a variety of applications.
Construction of Motion Controller
The construction of a motion controller can vary depending on the specific design and intended use. However, here is a general overview of the construction components:
- Housing: The outer casing or housing of the motion controller provides physical protection and houses the internal components. It is generally designed to be ergonomic for comfortable use.
- Sensors: These are the basic components responsible for capturing motion data. Accelerometers measure speed, gyroscopes detect rotational motion, and magnetometers determine the direction of the device in relation to the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Microcontroller or processor: The brain of the motion controller, the microcontroller or processor, processes the data from the sensors. It interprets motion signals and translates them into actionable commands for the connected system.
- Communication Module: This component facilitates communication between the motion controller and the device or system it is controlling. This can be a wired connection, such as USB, or a wireless connection, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Power Supply: Motion controllers require a power source to function. It can be powered by batteries (rechargeable or disposable) or a wired power connection.
- Buttons and Controls: Many motion controllers feature additional buttons, triggers, or touch-sensitive areas to provide users with alternative input methods beyond motion sensing.
- Feedback mechanisms: Advanced motion controllers may include haptic feedback components, such as vibration motors, to simulate touch or force feedback, to improve the user experience.
- Microswitches or mechanical components: Buttons and triggers often rely on microswitches or other mechanical components to accurately register user input.
- Circuitry and PCBs: Internal circuitry and printed circuit boards (PCBs) connect and integrate the various components, allowing them to work together seamlessly.
Building a motion controller involves careful consideration of the intended purpose of the device, the user experience, and the technologies involved to ensure accurate and reliable motion sensing.
Working of Motion Controller
The job of a motion controller involves several steps to capture, interpret and respond to motion input. Here’s a simple overview:
Motion Detection: The motion controller is equipped with sensors, such as an accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. These sensors continuously measure changes in speed, rotation and direction.
Sensor Data Processing: Raw data from the sensors is sent to the motion controller’s microcontroller or processor. This processing unit interprets the data taking into account the type and direction of movement.
Translation of Motion to Commands: The microcontroller translates the interpreted motion data into specific commands or actions based on predefined mapping or programming. For example, tilting a controller forward can be mapped to moving a character forward in a game.
Communication with the system: The motion controller transmits these translated commands to the connected device or system. This communication can be through a wired connection such as USB or a wireless connection such as Bluetooth.
Integration with buttons and controls: In addition to motion sensing, many controllers have buttons, triggers, or touch-sensitive areas. The microcontroller integrates the input from these controls with the motion data, providing a comprehensive input system.
User feedback: Some motion controllers include feedback mechanisms, such as vibration or haptic feedback, to provide users with tactile sensations in response to their actions. This adds to the immersive experience and ensures successful input.
Power Management: A motion controller requires a power source, usually provided by batteries or a power connection. Power management systems ensure efficient use of energy to prolong the operational life of the controller.
Software Integration: The connected system, whether it’s a gaming console, virtual reality headset, or other device, interprets incoming commands and responds accordingly. This integration requires compatible software and drivers.
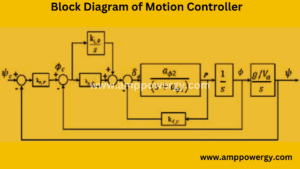
Overall, the function of a motion controller depends on a combination of sensors, processing units, communication interfaces, and feedback mechanisms to seamlessly translate physical movements into meaningful actions within a digital environment.
Uses of Motion Controller
Motion controllers have a wide range of applications in various industries and sectors. Here are some common uses:
- Gaming: Motion controllers are widely used in the gaming industry to provide a more immersive and interactive gaming experience. Players can control characters and actions in the game by physically moving the controller.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Motion controllers play an important role in VR and AR environments, allowing users to interact with virtual objects and environments by mirroring their real-world movements. allowed to do.
- Robotics: In robotics, motion controllers are used to control the movements of robotic arms and other devices. They enable precise and coordinated movement for tasks such as pick-and-place operations or assembly.
- Simulations and Training: Motion controllers are used in simulation and training programs to simulate real-world scenarios. This is common in aviation and military training, where realistic motion feedback enhances the training experience.
- Medical Applications: Motion controllers are used in medical devices and rehabilitation equipment. They help control robotic prosthetic devices, rehabilitation devices, and surgical robots.
- Industrial Automation: Motion controllers are essential in industrial automation to control the movement of machinery and manufacturing equipment. They ensure accurate and coordinated movement in the production process.
- Smart home devices: Some smart home devices use motion controllers for user interaction. For example, motion-controlled lights or smart thermostats can respond to specific gestures or movements.
- Motion Capture Systems: In the entertainment industry, motion controllers are an important component of motion capture systems. They capture the movements of actors and translate them into digital animation for films, video games and virtual productions.
- Sports and fitness: Motion controllers are used in sports and fitness applications, providing real-time feedback on movement for training purposes or interactive fitness experiences.
- Accessibility: Motion controllers can be adapted for use in assistive technology, helping people with disabilities control devices or interact with computers using their body movements.
Advantages of Motion Controller
- Dynamic interaction: Motion controllers provide a more immersive and natural way to interact with digital environments, especially in gaming and virtual reality applications.
- Improved Gameplay: In gaming, motion controllers can offer a more dynamic and exciting gameplay experience, allowing players to physically interact with the game world.
- Accuracy and precision: Motion controllers, when designed well, can offer accurate and precise movement tracking, allowing for more realistic and responsive control.
- Versatility: Motion controllers have diverse applications in a variety of industries, from gaming and entertainment to healthcare, robotics and industrial automation.
- Accessibility: Motion controllers can increase accessibility in technology, giving people with disabilities alternative ways to interact with devices and systems.
- Training and Simulation: In fields such as aviation, military and medical training, motion controllers facilitate realistic simulation and training scenarios.
Disadvantages of Motion Controller
- Learning curve: Users may need time to adapt to motion controls, and there may be a learning curve associated with mastering the necessary gestures or movements.
- Limited accuracy in some cases: In some applications, motion controllers may lack the accuracy necessary for complex tasks, which may lead to limitations in some professional or industrial settings.
- Dependence on sensors: Motion controllers rely heavily on sensors, and if these sensors become damaged or lose calibration, it can affect the accuracy and functionality of the controller.
- Power consumption: Some motion controllers, especially wireless controllers, can have high power consumption, requiring frequent battery changes or recharges.
- Cost: Advanced motion controllers with high-quality sensors and features can be expensive, which may limit their widespread adoption in some markets.
- Space requirements: Effective use of motion controllers often requires sufficient physical space for users to move around without obstructions, which can be a challenge in some environments.
- See Also:
- Force Sensing Resistor
- Avalanche Photodiode
- How to Change O2 Sensor?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a motion controller?
Ans: A motion controller is a device that interprets and responds to physical movements, allowing users to interact with a digital environment or control system through motion signals.
Q: How do motion controllers work?
Ans: Motion controllers typically use sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers to detect motion. Data from these sensors is processed, translated into commands, and delivered to a connected device or system.
Q: What Industries Use Motion Controllers?
Ans: Motion controllers find applications in gaming, virtual reality, robotics, industrial automation, healthcare, simulation, and entertainment, among other industries.
Q: What are the advantages of using motion controllers?
Ans: Benefits include excellent interactivity, improved gameplay, accuracy and precision, versatility in applications, accessibility, and effective use in training and simulation.
Q: Are motion controllers only used for gaming?
Ans: No, motion controllers have diverse applications beyond gaming, including virtual reality experiences, industrial automation, medical devices, simulations, and more.
Q: Do all motion controllers require external sensors?
Not Ans: required. While some motion controllers use external sensors for tracking, others have built-in sensors. The choice depends on the specific design and application.
Q: Are motion controllers wireless or wired?
Ans: Motion controllers can be both wireless (using technologies such as Bluetooth) and wired (such as USB-connected controllers). The choice depends on the specific use case and design.
Q: Can motion controllers be used for accessibility purposes?
Ans: Yes, motion controllers can be adapted for accessibility, providing people with disabilities alternative ways to interact with devices and systems.
Q: Do motion controllers require a learning curve?
Ans: Yes, users may need some time to adapt to motion control, especially if the required gestures or movements are new to them.
Q: What are the limitations of motion controllers?
Ans: Limitations may include learning curves, potential accuracy issues in some applications, dependence on sensors, power consumption, cost, and space requirements for effective use.
