What is a Resistance Temperature Detector
It is an electronic device which is used to find the temperature of the wire by measuring its resistance. The wire works as a temperature sensor. RTD measures the temperature with high accuracy. RTD has a good linear characteristic. Thermocouple and thermistor are also used to measure the temperature.
If the resistance of the metals varies when variation comes in the temperature, then the equation will be.
this equation is for high rang of temperature.
this equation is for high rang of temperature.
Rt and R0 is the value of the resistance at the rang od temperature as tCº and t0Cº
If the rang of the temperature is low, then this equation will use
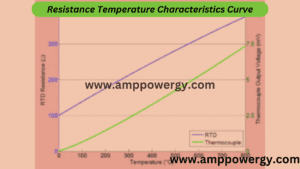
Copper, nickel and platinum are widely used metals in the RTD devices. Resistance variation comes in these metals with variation of temperature is totally different. And this is the resistance temperature characteristics of the materials.
The temperature range of platinum is 650 0C and the temperature range of platinum 1200C and nickel is 3000C. If per degree change comes in the temperature, 0.4-ohm change comes in the resistance of the platinum.
To check the purity of the platinum divide R100 by R0 (R100/R0). The materials which are used to make RTD from should be pure because if the materials are not pure then it will deviate from the conventional resistance temperature graph and the values of alpha (α) and beta (β) will change based upon the metals.
The change in the resistance is due to a change in the temperature and this change is described by an equation. Let’s take an example of most using RTD in the market which is Pt100 (t stand for platinum and 100 stand for ohm)
Equation for this RTD is
R is resistance and T is temperature
To solve the above equation for T
The figure shows the resistance temperature characteristics.
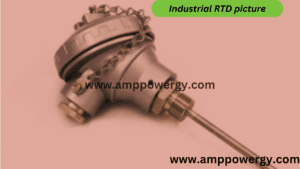
Construction of the Resistance Temperature Detector
The construction of the RTD is like a wire wound around in the form of coil on a mica frame. It is wound around is such that to achieve a small size to increase its thermal conductivity and decrease its response time. And a high amount of heat transfer is obtained from it. The RTDS is used in industries, its coil is protected by stainless steel or sometimes use protective tube used for it.
Now if any change comes in the temperature the wire expands because of heat due to this the physical stain come in the wire which is negligible. Now if the wire strain increases the tension increases due to this the wire resistance is change and this is undesirable because changes in the resistance is not allowed in the RTD. For better insulation the mica is placed in between the resistance wire and the steel. sheath. There is less stain in the resistance wire so make RTD it would be carefully wound around the mica.
Signal conditioning of RTD
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
There are multiple RDT Is available in the market, but the most important thing is to know the procedure of using it to minimize the lead wire and calibration errors. The change in the resistance is very small due to temperature in industrial RTDs.
The value of RTD is measured by bridge circuit. The constant electric current is supplied to the bridge circuit which results in the voltage drops in the resistor which is to be measured by the circuit and the resistance of the RTD is calculated this way. The temperature also needs to be determined. To determine the temperature, convert the resistance of RTD by calibration equation.
Different module of RTD
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
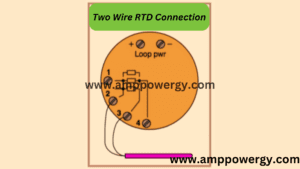
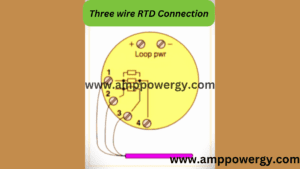
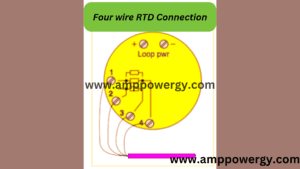
The dummy wire is absent in the two wire RTD. So, the output is taken from the two wires. The extension wire resistance is also important to be considered because its impedance can affect the temperature.
In three wire system this is minimized by connecting a dummy wire. The impedance effect will be cancelled because of opposite position if the wire A and B are matched in term of length and cross section area. The dummy wire in the three-wire bridge circuit acts like a sensor which measures the voltage drops in the resistance of RTD. The output voltage in the three-wire bridge circuit is directly proportional to the temperature, so the calibration equation is needed for measuring the temperature.
Equation for three wire RTD circuit
If the value of VS and V0 is given, we can determine Rg and then temperature can be found by using the calibration equation.
Now if R3=Rg, then V0=0 the bridge will be balanced.
Solve equation above to get equation for Rg.
RL = 0 in this equation
Now consider RL is present in the equation, then the equation will be.
because RLresistance errors can come in the RTD resistance, so we recompense RL resistance.
There is I²R power dissipation in the RTD device, which is called self-heating of RTD, and it can cause slight heating affect and it can bring some errors in the reading. To avoid self-heating the electric current in the RTD should be kept low and constant.
What is a Wheatstone bridge circuit
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
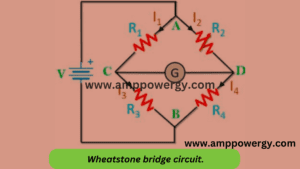
Wheatstone bridge circuit is used to measure the change in the resistance. It is the most common way to use while resistance can be measured by multimeter. In Wheatstone bridge circuit the RTD acts like a adjustable resistor and it can replace RX this as the resistance change the voltage can be measure. Now to measure the temperature change, circuit analysis and linear equation can be sued for it but the most common way to measure temperature change by calibration method.
The figure shows the Wheatstone bridge circuit.
How to calibrate the resistance temperature detector
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
Place RTD in ice bath, room temperature water, heated water and boiling water etc. and note the temperature reading on a thermometer and voltage on Wheatstone bridge circuit, repeat this process and note the reading, then plot these points and find a fit line which will show the relation between temperature and voltage. It will take time, but it is a very efficient method that automatically notes the temperature change on the wiring as the resistance change it means the RTD resistance is changing.
Advantage and limitation of RTD
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
It can show accurate temperature measurement value which does not change rapidly. So, it can be used for repeatable uses. Its response is slower than the other sensor because there are three heat transfer methods which I conduction, convection, and radiation.
In Conduction heat flow directly between solid materials and in convection heat is transfer because of moving of fluid while in radiation heat flow occurs due to wavelength.
These methods are slower in the RTD, because RTD is placed in evacuated chamber it means it cannot touch the heat directly. Radiation heat transfer can be possible, but it is used mostly in high temperature.
The resistance of the wires which are used to connect the RTD with measurement will increase with temperature, now if they are replaced with longer wire its resistance will increase and the total resistance will also increase.
RTD is a very efficient way to measure the temperature, but it cannot be used there, were temperature changes quickly.
Disadvantage of RTD
- RTD is high cost.
- RTD is large bulb size.
- RTD low sensitivity.
- Shok and vibration can affect RTD.
- RTD needs a complex circuit for measurement.
- RTD response time is slower than thermocouple.
- RTD temperature range is small.
- RTD power supply needs a bridge circuit to operate.
- RTD can lead to errors when high accuracy is needed.
- self-heating is possible in resistance temperature detector.
RTD uses in Industries
(What is a Resistance Temperature Detector)
- Industries which make food and beverages can use RTD for heating and refrigeration systems. To prevent the contamination products
- It can be used to monitor engine temperature, air take temperature, oil temperature etc.
- It can be used to measure amplifier and transistor temperature.
FAQS Frequently asked question about RTD
Q1: What is resistance temperature detector (RTD)?
Ans: resistance temperature detector (RTD) is a sensor whose resistance changes with temperature that is if temperature increase the resistance increase. It is a passive device which cannot produce output by itself.
Q2: how does resistance temperature detector (RTD) work?
Ans: RTD works on the base of resistor because the resistor is placed in the circuit which modulates the current in the circuit. RTD obey ohm law which is V= I R.
Q3: what is the recommended connection for PT100 RTD?
Ans: the recommended connection for PT100 is a 4-wire connection.
Q4: how to choose the alpha TCR curve?
Ans: it depends upon the instrumentation which is used. Japan use JIS curve and Europe use DIN curve.
See Also:

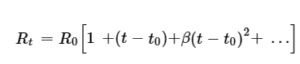
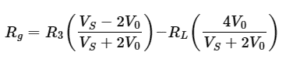
2 thoughts on “Resistance temperature detector (RTD) its Construction, Uses and Advantage”