What is an Automatic Voltage switcher?
An automatic voltage switcher, also called an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) or an automatic voltage stabilizer (AVS), is a device designed to regulate and stabilize the voltage supplied to electrical appliances and equipment. has gone Its main function is to ensure a constant and safe voltage level, protecting electronic devices from voltage fluctuations.
Fluctuations in voltage can be caused by various reasons, such as fluctuations in the power grid, sudden changes in load, or variations in the power supply. These fluctuations can potentially damage sensitive electronic equipment by providing too high or too low a voltage.
An automatic voltage switcher usually monitors the incoming voltage and adjusts it to maintain a stable output within a specified range. If the voltage exceeds or falls below acceptable limits, the device automatically corrects itself to bring the voltage back to the desired level. It helps protect the connected devices and ensures their proper functioning.
Automatic voltage switchers are commonly used in homes, offices and industrial settings where a stable power supply is essential for reliable operation of electronic equipment. They are particularly useful in areas with unreliable power grids or frequent voltage fluctuations.
Construction of Automatic Voltage Switcher
The construction of Automatic Voltage Switcher (AVS) or Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) depends on the specific design and manufacturer. However, I can provide a general overview of the components commonly found in these devices:
Voltage Sensor: It is a component that measures the input voltage. This can be a voltage transformer or a solid-state sensor.
Control Circuit: The control circuit processes the information from the voltage sensor and determines whether the input voltage is within the acceptable range or not. It then sends signals to other components to adjust if necessary.
Transformer or Buck Boost Circuit: To regulate voltage, AVS often uses a transformer or buck boost circuit. A transformer can increase or decrease the voltage as needed to maintain a stable output.
Voltage Comparator: A voltage comparator compares the measured voltage with a reference voltage. If the input voltage deviates from the set range, the comparator signals the control circuit to take corrective action.
Adjustment mechanism: It can be a manual or automatic adjustment mechanism that allows users to set the desired output voltage or automatically adjusts it based on the detected input voltage.
Switching devices: These are electronic switches or relays that control the flow of electricity and regulate the output voltage.
Display and Interface: Many AVS devices have a display to indicate device status indicators as well as input and output voltage levels. Some also come with a user interface to adjust the settings.
Protection Circuitry: AVS units often include safety features such as surge protection, overvoltage protection, and other safety measures to protect connected equipment.
Enclosure: Components are usually housed in a protective enclosure to ensure safety and durability.
It is important to note that the specific design and features of automatic voltage switchers may vary between manufacturers and models. Additionally, more advanced models may incorporate microcontrollers or other smart technologies for better functionality. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for detailed information on a particular AVS unit.
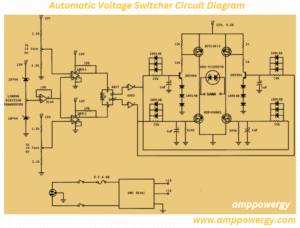
Mathematical Relations in Automatic Voltage Switcher
An automatic voltage switcher (AVS) involves monitoring and regulating voltage levels in mathematical relationships. Although the exact mathematical models may vary based on the specific design and technology used by different manufacturers, some general mathematical relationships are involved in the operation of AVS units:
Voltage Sensing:The relationship between the sensed input voltage (Vin) and the reference voltage (Vref) is important. Vin compares with Vref to determine if the input voltage is within acceptable limits.

Control and Adjustment Mechanism:The control circuitry adjusts the output voltage based on the comparison results. An adjustment mechanism, which may include a transformer or buck-boost circuit, modifies the voltage to bring it within an acceptable range.
![]()
Voltage comparison:A voltage comparator can use mathematical conditions to trigger corrective actions. For example, a simple comparison can be defined as:

Response time:The response time of an AVS can be modeled mathematically, which describes how quickly the system adjusts the output voltage in response to changes in the input voltage.
![]()
Capacity and load:The capacity of the AVS unit and the load it can handle are important parameters. Mathematical relationships include the maximum current (I) or power (P) that the AVS can support.
Display Reading:If the display is in AVS, the relationship between the measured values and the displayed values involves a mathematical transformation or scaling.
![]()
These mathematical relationships help explain the behavior of AVS in response to various input conditions. The exact equations and algorithms used may vary based on the specific design and characteristics of the AVS unit. Manufacturers usually provide detailed specifications and documentation that outline the mathematical principles and algorithms used in their devices.
Working of Automatic Voltage Switcher
The principle of operation of an automatic voltage switcher (AVS) involves monitoring the incoming voltage, comparing it to a fixed reference, and adjusting maintain a stable output voltage within a predetermined range. Is. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how AVS works in general:
Voltage Sensing: AVS monitors the input voltage using a constant voltage sensor, which can be a transformer or a solid state sensor. The sensor detects the voltage level of the incoming power supply.
Reference Voltage Comparison: The measured voltage is compared to a predetermined acceptable voltage range using a reference voltage or voltage comparator. This reference voltage is set to the desired output voltage.
Control Circuit: The control circuit processes the information from the voltage comparator. If the input voltage is within the acceptable range, no action is taken. However, if the voltage exceeds the specified limits, the control circuit activates the adjustment mechanism.
Adjustment mechanism: Depending on the design, the adjustment mechanism can be manual or automatic. In an automatic system, an adjustment mechanism, which may be a transformer or a buck-boost circuit, modifies the voltage to bring it back within an acceptable range.
Switching devices: Electronic switches or relays are used to control the flow of electricity and regulate the output voltage. When adjustments are required, these switching devices facilitate the necessary changes in the electrical circuit.
Display and Indicators: Many AVS units have a display that shows input and output voltage levels. Indicators can also indicate the status of the device, such as whether it is operating normally or if there is a problem.
Protection Features: AVS units often come with built-in protection features, such as surge protection and overvoltage protection, to protect connected devices from potential damage.
Continuous monitoring: AVS continuously monitors the input voltage and makes real-time adjustments to ensure a stable and safe output voltage.
The overall purpose of an AVS is to provide a constant and safe voltage supply to connected electronic devices, protecting them from voltage fluctuations that might otherwise cause malfunction or damage. Automatic voltage switchers are commonly used in homes, offices and industrial settings to ensure reliable operation of electrical equipment despite variations in power supply.
Application of Automatic Voltage Switcher
Automatic Voltage Switchers (AVS) find applications in various settings where a stable and regulated power supply is important for the proper operation and protection of electrical equipment. Some common applications include:
Residential Use: Home Electronics: AVS units are used to protect sensitive home electronics, such as televisions, refrigerators, computers, and audio equipment, from voltage fluctuations.
Commercial and Office Environment:Computers and Servers: AVS devices are used to protect servers, computers and other IT equipment from voltage fluctuations, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Printers and copiers: Sensitive office equipment benefits from a stable power supply to prevent damage and maintain consistent performance.
Industrial Settings:Manufacturing Equipment: Industrial machinery, including CNC machines and other manufacturing equipment, often requires constant power to prevent interruptions and ensure accuracy in operations.
Control Systems: Automation and control systems in industrial processes depend on stable voltage levels to avoid errors and malfunctions.
Medical facilities:Medical Equipment: Sensitive medical equipment such as diagnostic equipment, imaging systems, and life support machines rely on stable power sources provided by AVS units to prevent malfunction or damage.
Telecommunications:Communication infrastructure: AVS is used to protect critical telecommunication equipment, such as switches, routers, and communication servers, from voltage fluctuations.
Laboratories:Scientific instruments: Laboratories often use sensitive scientific instruments that require a stable power supply to maintain accurate measurements and experiments.
Data Centers:Server Rooms: AVS devices are essential in data centers to ensure that servers and networking equipment receive a constant and stable power supply, minimizing the risk of data loss or hardware damage.
Remote and Unstable Power Grid Areas:
Off-grid locations: In areas with unreliable or fluctuating power grids, AVS units can be used to stabilize voltage for critical applications, such as remote communication stations or off-grid installations.
HVAC System:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC): Some HVAC systems may incorporate AVS units to protect control systems and electronic components from voltage fluctuations.
Audio Visual Equipment:Concerts and Events: AVS devices are used to protect audio-visual equipment at events and performances where stable power is critical for a smooth and uninterrupted show.
In summary, automatic voltage switchers are widely used in residential, commercial, industrial and special settings, where maintaining a stable power supply is essential for the reliable operation and protection of electronic equipment.
Advantages of Automatic Voltage Switchers (AVS):
Protection from voltage fluctuations: The main advantage of AVS is the ability to protect electrical and electronic equipment from voltage fluctuations, ensuring stable and constant power supply.
Better equipment life: By maintaining a stable voltage, AVS helps extend the life of connected equipment and reduces the risk of premature failure due to overvoltage or undervoltage conditions.
Automatic Operation: AVS units operate automatically, eliminating the need for constant manual monitoring and adjustments. This makes them convenient and user-friendly.
Wide range of applications: AVS devices can be used in a variety of settings including homes, offices, industrial facilities, medical facilities and more, making them versatile in handling a variety of power supply challenges.
Surge Protection: Many AVS units come with surge protection features, which protect connected devices from sudden voltage spikes.
Consistent Performance: AVS ensures consistent performance of electronic equipment and prevents interruptions due to voltage fluctuations, especially in critical applications such as data centers, medical facilities, and industrial processes.
Disadvantages of Automatic Voltage Switchers (AVS):
Initial Cost: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing AVS units can be prohibitive for some customers. Higher capacity or more advanced models may be more expensive.
Limited capacity: AVS units may have limitations in terms of the maximum load they can handle. Consumers need to choose a unit with the appropriate capacity for their specific needs.
Maintenance Requirements: While AVS units generally require minimal maintenance, occasional checks and inspections may be required to ensure proper operation. Dust accumulation or component wear over time can affect performance.
Response Time: In some situations, the response time of an AVS unit can be critical to correct voltage fluctuations. Some devices may have a slight delay in adjusting the voltage, which may be a concern for sensitive equipment.
Not a substitute for an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Although an AVS can regulate voltage, it does not provide a backup power source during power outages. For continuous power during outages, UPS (uninterruptible power supply) is required.
Complexity in troubleshooting: If the AVS unit malfunctions, technical expertise may be required for troubleshooting and repair. Consumers may need to consult the manufacturer’s instructions or seek professional assistance.
In summary, the advantages of AVS, such as protection against voltage fluctuations and increased equipment life, make them valuable in a variety of applications. However, potential disadvantages include initial cost, limited capacity, and the need for occasional maintenance. Consumers should carefully consider their specific needs and the capabilities of different AVS models before making a decision.
See Also:
Frequently Asked Question FAQs
Q: What is Automatic Voltage Switcher (AVS)?
Answer: An AVS is a device designed to regulate and stabilize the voltage supplied to electrical appliances and equipment, protecting them from voltage fluctuations.
Q: How does AVS work?
Answer: AVS units monitor the incoming voltage, compare it to a fixed reference, and make adjustments to maintain a stable output voltage within a predetermined range. This is achieved through a combination of voltage sensing, comparison, and adjustment mechanisms.
Q: What types of devices benefit from AVS protection?
Answer: AVS is beneficial for a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, servers, audio-visual equipment, refrigerators, medical equipment, and industrial machinery.
Q: What are the benefits of using AVS?
Answer: AVS protects connected equipment from voltage fluctuations, extends equipment life, operates automatically, provides surge protection, and ensures consistent performance.
Q: Is AVS the same as UPS (uninterruptible power supply)?
Answer: No, AVS and UPS serve different purposes. AVS regulates voltage to protect against fluctuations, while UPS provides a backup power source during outages.
Q: Do AVS units require manual adjustment?
Answer: Many AVS units operate automatically, adjusting voltage levels without manual intervention. Some models may have manual adjustment options for user customization.
Q: Can AVS units handle different voltage inputs?
Answer: AVS units are designed to handle a range of input voltages, making them suitable for use in different areas with different power supply conditions.
Q: What happens during a power outage with AVS?
Answer: AVS units do not provide backup power. They regulate voltage but cannot supply power during outages. For uninterrupted power during outages, UPS is required in conjunction with AVS.
Q: Can AVS protect against lightning strikes?
Answer: Although some AVS units may offer surge protection, protection against direct lightning strikes usually requires additional measures, such as lightning arresters and grounding.
Q: Are AVS units compatible with all types of electrical appliances?
Answer: AVS units are generally compatible with a wide range of electrical and electronic equipment. However, users should check the AVS capacity and features to ensure it meets their equipment needs.
Q: Do AVS units require regular maintenance?
Answer: While AVS units generally require minimal maintenance, periodic checks may be recommended to ensure proper operation. Dust accumulation or wear on components can affect performance over time.
