What is Servo Motor and its Function?
A servo motor is a type of electromechanical device that works by using feedback control to precisely control the position, velocity, and speed of a mechanical system. It consists of a motor with a sensor (such as an encoder or resolver) and a control circuit. The control circuit receives an input signal, usually in the form of a desired position or speed and adjusts the output of the motor to achieve and maintain the desired state.
Servo motors are widely used in a variety of applications that require precise and responsive motion control, such as robotics, CNC machinery, automation systems, camera stabilization systems, and aircraft control surfaces.
They offer high accuracy, fast response times, and the ability to operate at a wide range of speeds and torques. Additionally, servo motors are often characterized by their closed-loop control systems, where feedback from sensors is used to continuously adjust the motor’s operation, ensuring accurate positioning and motion control.
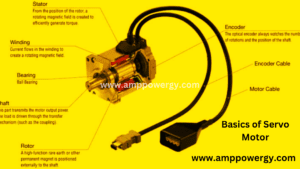
Parts of Servo Motor
Servo motors usually consist of several key components that work together to precisely control the movement of the motor. Here are the main parts of a servo motor:
Motor: A servo motor component usually consists of a DC motor, although some servo motors may use brushless DC motors or other motor types. The motor generates the mechanical power necessary to operate the system.
Gear Train: Many servo motors incorporate a gear train to reduce the speed of the motor and increase its torque output. A gear train consists of a series of gears that transmit motion from the motor to the output shaft with increasing torque and low speed.
Feedback device: A feedback device provides information to the control system about the current position, speed and/or speed of the motor. Common types of feedback devices used in servo motors include encoders, resolvers, and potentiometers.
Control Circuit: The control circuit is responsible for processing the input signals and generating output signals to control the operation of the motor. It usually includes a microcontroller or other electronic component that implements a control algorithm to regulate the speed and position of the motor based on feedback from a feedback device.
Driver Circuit: The driver circuit amplifies the control signals generated by the control circuit to provide the power required to drive the motor. This ensures that the motor receives the proper voltage and current to achieve the desired performance.
Output Shaft: The output shaft is the component of the servo motor that rotates to perform mechanical work. It usually connects to the load or system to be controlled and transmits motion and torque to the desired mechanism.
Housing: The housing encloses and protects the internal components of the servo motor. It is usually made of metal or plastic and provides structural support and protection against environmental factors.
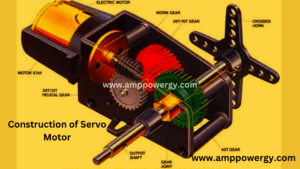
Construction of a Servo Motor
The construction of a servo motor usually involves a number of key components arranged in a specific order to provide precise control over the movement of the motor. Here is a breakdown of the general construction of a servo motor:
Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor and contains electromagnets or permanent magnets that generate the magnetic field. The stator provides the primary magnetic field that interacts with the rotor to produce motion.
Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is located inside the magnetic field of the stator. It usually consists of a shaft and rotor core made of magnetic material. The rotor may also include windings or magnets depending on the motor design.
Feedback device: Most servo motors incorporate a feedback device such as an encoder or resolver to provide feedback on the motor’s position, velocity, and/or speed. A feedback device enables closed-loop control, allowing the motor to accurately follow input commands.
Control Electronics: Control electronics include microcontrollers or other electronic components that are responsible for processing input signals and generating output signals to control the operation of the motor. Control electronics implement control algorithms to regulate motor speed and position based on feedback from a feedback device.
Driver Circuit: The driver circuit amplifies the control signals generated by the control electronics to provide the power required to drive the motor. This ensures that the motor receives the proper voltage and current to achieve the desired performance.
Driver Circuit: The driver circuit amplifies the control signals generated by the control electronics to provide the power required to drive the motor. This ensures that the motor receives the proper voltage and current to achieve the desired performance.
Output Shaft: The output shaft is the component of the servo motor that rotates to perform mechanical work. It usually connects to the load or system to be controlled and transmits motion and torque to the desired mechanism.
Housing: The housing encloses and protects the internal components of the servo motor. It is usually made of metal or plastic and provides structural support and protection against environmental factors.
Bearings: Bearing are used to support the shaft of the rotor and to allow the rotor to rotate smoothly within the housing of the motor. They reduce friction and wear, ensuring efficient operation of the motor.
These components work together to provide precise control over the motor’s motion, making servo motors suitable for applications requiring precise positioning, velocity and speed control. The specific design and configuration of a servo motor may depend on factors such as the intended application, performance requirements, and manufacturer specifications.
Function of Servo Motor
A servo motor is a type of rotary actuator or motor that allows precise control of angular position, velocity and speed. the function of servo motor is followed:
Position Control: Servo motors are mainly used to control the position of an object or mechanism. They can rotate to a specific angle and hold that position precisely, making them ideal for applications where precise positioning is required, such as robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation.
Feedback mechanism: Servo motors usually include a feedback mechanism, such as an encoder or potentiometer, that provides information about the current position of the motor. This feedback loop allows for closed-loop control, where the controller can continuously adjust the output of the motor to achieve and maintain the desired position.
Variable speed: Servo motors can operate at variable speed, allowing for smooth and precise motion control. By adjusting the input signal, the speed of the motor can be precisely controlled.
Torque Control: Servo motors can provide variable amounts of torque depending on the application requirements. This torque can be controlled manually or automatically by an input signal to the motor.
Compact and lightweight: Servo motors are often more compact and lightweight than other types of motors with similar power ratings, making them suitable for applications where space and weight are constraints.
High accuracy and repeatability: Servo motors offer high accuracy and repeatability in positioning, making them well suited for applications that require precise motion control, such as 3D printing, camera Stability systems, and robotic arms.
Overall, the function of a servo motor revolves around precise control of position, speed, and torque, making it a versatile and essential component in various electromechanical systems.
Uses of Servo Motor
Servo motors find applications in various industries and technologies where precise control of position, velocity and speed is required. the following are the uses of servo motor:
Robotics: Servo motors are widely used in robotic systems to control joints, grippers and other moving parts. They enable precise and flexible motion control, making them essential for tasks such as pick-and-place operations, assembly and manipulation.
CNC Machinery: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, including CNC rotors, mills, lathes, and 3D printers, to control the movement of cutting tools and workpieces with high precision and repeatability. Use servo motors.
Automated Manufacturing: Servo motors play an important role in automated manufacturing systems for tasks such as conveyor belt control, packaging, sorting, and material handling. They ensure accurate positioning and coordination of moving parts in production lines.
Camera stabilization: Servo motors are used in camera stabilization systems, such as gimbals and stick Cam, to stabilize camera movements and ensure smooth, shake-free footage during filming or photography.
Aerospace and Defense: Servo motors are used in aircraft control surfaces, including ailerons, elevators, and rudders, to precisely adjust the aircraft’s attitude and movements. They are also used in missile guidance systems, radar antennas, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Medical Devices: Servo motors are used in a variety of medical devices and equipment, including surgical robots, imaging systems, prostheses, and patient positioning systems. They provide precise motion control for accurate and safe medical procedures.
Automotive Systems: Servo motors are used in automotive applications such as power steering systems, throttle control, brake-by-wire systems and active suspension systems. They help improve vehicle performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
Satellites and spacecraft: Servo motors are used in satellite and spacecraft systems for tasks such as solar panel deployment, antenna positioning, and attitude control. They provide precise control over spacecraft orientation and subsystem operations.
These are just a few examples of the diverse uses of servo motors in different industries and technologies. Their ability to provide precise and responsive motion control makes them indispensable in modern automation, robotics and control systems.
Servo motors offer several advantages and disadvantages over other types of motors. Here’s a breakdown:
Advantages of Servo Motor
High precision: Servo motors provide precise control over position, velocity, and speed, making them ideal for applications requiring precise motion control.
Fast response: Servo motors have low inertia and a high torque-to-instance ratio, allowing fast acceleration and deceleration in response to input commands.
Closed-loop control: Servo motors typically operate in a closed-loop control system, where feedback from encoders or other sensors is used to continuously adjust the motor’s performance, ensuring accurate positioning and motion control. is made.
Variable Speed: Servo motors can operate over a wide range of speeds, allowing flexibility in controlling the speed and velocity of moving parts in a variety of applications.
High torque-to-size ratio: Servo motors often have a high torque-to-size ratio, providing significant power output in a compact and lightweight package.
Low maintenance: Servo motors typically have fewer moving parts than other types of motors, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and longer service life.
Disadvantages of Servo Motor
Complexity: Servo motor systems can be more complex and expensive than simple motor types, especially when implementing closed-loop control systems with feedback devices.
Cost: Servo motors and associated control systems are more expensive than other motor types, especially for high-performance applications that require precision and reliability.
Power consumption: Servo motors can consume more power than other types of motors, especially when operating at high speeds or under heavy loads.
Noise and Vibration: Servo motors can generate noise and vibration during operation, especially at high speeds or when driving heavy loads, which may require additional measures for noise reduction and vibration damping.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Servo motors can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can interfere with nearby electronic equipment or communication systems if not properly shielded.
See Also:
- What is turbine and its Function?
- What is the Difference between Francis and Kaplan turbine?
- what are wind turbine and their uses?
Frequently Asked Question
What is a servo motor?
A servo motor is a rotary or linear actuator that allows precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and speed. It consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback, usually using a closed-loop control system.
How does a servo motor work?
Servo motors work by receiving a control signal that specifies a desired position or speed. The motor then adjusts its shaft to move into that position based on feedback from an encoder or potentiometer. This closed loop control system ensures accurate positioning.
What are the parts of a servo motor?
The main components of a servo motor include the motor itself (usually a DC motor or brushless DC motor), a gearbox (in some cases), a feedback device (such as an encoder or potentiometer), control electronics, and sometimes position control. Loops are included.
What are the advantages of using servo motors?
Servo motors offer precise control over position, velocity, and speed, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability. They also have a high torque to inertia ratio, which means they can accelerate and decelerate quickly.
What are some common applications of servo motors?
Servo motors are used in a wide range of applications including robotics, CNC machines, industrial automation, aerospace, automotive systems, camera gimbals, and 3D printers.
briefly explain the differences between a servo motors and stepper motor?
Although both servo motors and stepper motors are used for motion control, servo motors generally offer higher efficiency and greater accuracy. Stepper motors move in discrete steps, while servo motors can run smoothly and continuously.
which factors should be considered when selecting a servo motor?
When selecting a servo motor, factors to consider include torque requirements, speed requirements, accuracy, size constraints, environmental conditions, and overall system dynamics.
Can servo motors be used for continuous rotation?
While servo motors are primarily designed for precise angular positioning, some models can be modified for continuous rotation by removing the mechanical stops and adjusting the control system accordingly.
What are some common troubleshooting techniques for servo motors?
Common troubleshooting techniques for servo motors include checking for mechanical binding or impedance, verifying wiring connections, adjusting control parameters, and ensuring proper power supply voltage. Additionally, it is important to check the feedback device for accuracy and integrity.
