What is the Function of Thermocouple?
Definition:
A thermocouple is like a sensor which is used to measure temperature. A thermocouple consists of two types of metal wires which are joined together to form a junction. When there’s a temperature gradient between the joined end (the hot junction) and the open ends (the cold junctions), it generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference. When the voltage is measured, it is then converted to temperature reading.
Thermocouples are widely used because they are relatively inexpensive, rugged, and can operate in a wide range of temperatures. They find applications in various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and home appliances.
Function of the Thermocouple:
A step-by-step explanation of thermocouple function:
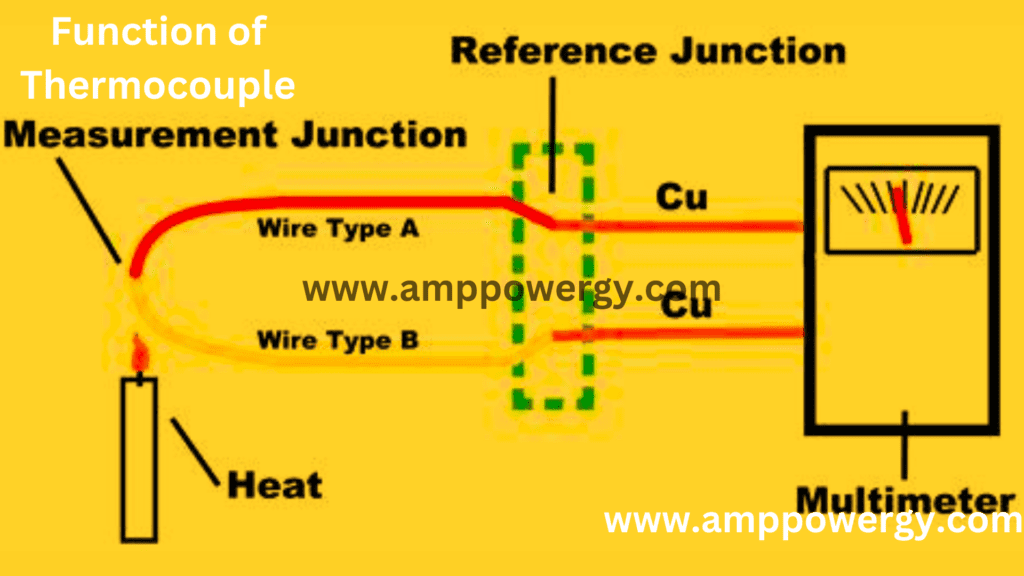
Two Different Metals: A thermocouple consists of two different types of metal wires joined together at one end to form a junction. This junction is often referred to as the “hot junction” or “measuring junction.”
Temperature Gradient: The hot junction of the thermocouple is exposed to the temperature that needs to be measured. Meanwhile, the other ends of the metal wires, known as the “cold junctions,” remain at a reference temperature, usually the ambient temperature of the environment.
Seebeck Effect: When there’s a temperature difference between the hot junction and the cold junctions, an electric voltage is generated across the ends of the thermocouple wires.
Voltage Measurement: The generated voltage is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the hot and cold junctions according to the Seebeck effect. This voltage can be measured using a voltmeter or other electronic instruments.
Conversion to Temperature: By using a calibration curve or a lookup table specific to the type of thermocouple being used, the voltage reading obtained from the thermocouple can be converted into an accurate temperature measurement.
Temperature Monitoring: The converted temperature reading provides real-time information about the temperature at the hot junction of the thermocouple. This data can be utilized for various purposes such as process control, monitoring, and safety in a wide range of applications across different industries.
Overall, the thermocouple operates by exploiting the Seebeck effect to generate a voltage signal proportional to the temperature difference, which is then measured and converted into a temperature reading for practical use.
What is Seebeck Effect:
The Seebeck effect is a fundamental phenomenon in physics discovered by German physicist Thomas Johann Seebeck in 1821. It describes the generation of a voltage difference (also known as an electromotive force or EMF) between two points in a conductor or semiconductor when there’s a temperature difference between them. Here’s how it works:
Temperature Difference: When there is a temperature gradient along the length of a conductor or across the junction of two different conductors, electrons in the material gain kinetic energy at the higher temperature end and lose energy at the colder end.
Asymmetric Electron Distribution: This temperature-induced kinetic energy difference causes a net migration of charge carriers, usually electrons, from the hotter end to the colder end. This movement of charge carriers creates an accumulation of negative charge at the cooler end and a deficit of electrons at the warmer end.
Generation of Voltage: The accumulation of charge at the cold end and the deficit of charge at the hot end creates an electric potential difference, or voltage, between the two ends of the conductor or junction. This voltage difference can be measured and is proportional to the temperature difference across the conductor or junction.
Proportional Relationship: The magnitude of the generated voltage is proportional to the temperature difference according to the material properties and geometry of the conductor or junction.
The Seebeck effect is the underlying principle behind the operation of thermocouples, which exploit this phenomenon to measure temperature. By connecting two different metals to form a thermocouple and subjecting them to a temperature gradient, a voltage is generated across the junction, which can be measured and correlated to the temperature difference.
How Do I Choose the Right Type of Thermocouple for my Application?
Selecting the appropriate type of thermocouple depends on various factors such as temperature range, environment, accuracy requirements, and compatibility with the measuring instrument.
- Temperature Range: Different types of thermocouples are suitable for different temperature ranges. Ensure the thermocouple you choose can operate within the temperature range of your application.
- Chemical Compatibility: Consider the chemical environment the thermocouple will be exposed to. Certain metals used in thermocouples may react with specific substances, affecting their performance and longevity.
- Accuracy Requirements: Determine the level of accuracy needed for your measurements. Some thermocouple types offer higher accuracy than others, especially in specific temperature ranges.
- Response Time: Consider how quickly you need the thermocouple to respond to temperature changes. Some types of thermocouples have faster response times than others.
- Cost and Durability: Balance your budget with the durability and lifespan of the thermocouple. Higher-grade thermocouples may have a longer lifespan and better performance but come at a higher cost.
How Does a Thermocouple Work to Measure Temperature?
A thermocouple operates based on the principle of the Seebeck effect, which describes the generation of a voltage when two dissimilar metals are joined together at one end and exposed to a temperature gradient. Here’s a brief explanation of how it works:
- Temperature Measurement: The thermocouple consists of two different metal wires joined together at one end to form a junction. This junction is usually exposed to the temperature that needs to be measured.
- Voltage Generation: When there’s a temperature difference between the junction (the hot end) and the open ends (the cold junctions), it creates an electric potential difference, or voltage, across the thermocouple wires which is proportional to the difference in the temperature.
- Measurement of Voltage: The generated voltage is measured using a voltmeter or other electronic instruments.
- Temperature Conversion: By using calibration curves or lookup tables specific to the type of thermocouple being used, the measured voltage can be converted into an accurate temperature reading.
- Real-Time Temperature Monitoring: The converted temperature reading provides real-time information about the temperature at the hot junction of the thermocouple.
See Also

1 thought on “What is the Function of Thermocouple?”