thin film resistor or what is thin film resistors: in this article you will read all about it.
What are Thin Film Resistors
First of all, lets know about what resistor is and its applications.
what is mean by a resistor?
A resistor is a device which regulateor limit the flow of current in the electrical circuit.it is the important components of the electronic circuits. The resistor has two terminals which are connected by trace or wire to the electrical circuit. The resistance is measured in ohm (Ω), which Is the ratio of voltage across the resistor to the current. The higher the resistance of the resistor the lower the voltage will be.
There are different types of resistors, which include fixed resistors, variable resistors, linear andnon-Lenier resistors.
What is the Application of Resistor
Resistors are used for different purposes in electronic devices such as adjusting signal level, reducing current flow, dividing voltages, biasing active elements, terminating transmission line, etc. Resistors are used to create simple circuit e.g., voltage divider, pull up and pull-down resistors, RC filters and current limiter.
What are Different Types of resistors
There are different types of resistors which are used in different places for different purposes in electronic circuits. These resistors have different properties depending upon their construction. These resistors are available in different shapes, sizes, and made from different materials but normally resistors are classified into two types which are linear resistors and nonlinear resistors.
Resistors are the fundamental electronic and electrical devices which are used in electrical circuits. Generally, resistors are designed to restrict the flow of the current in the electrical circuit. Film technology has come to replace the old Corbon resistor. Film resistors are classified into two types, thin film and thick film resistor. This article will explain the thin film resistor.
What is Thin Film Resistor?
Thin film resistor is known as a thin film resistor because a thin film layer of resistance is placed on the top of the ceramic base. The thickness of the thin film resistor is less as compared to the thick layer resistor which is around 0.1 microns. These resistors are stable, accurate, and have good temperature coefficient therefore used widely in various technologies. Both resistors are the same in shape, but manufacturing processes are different.

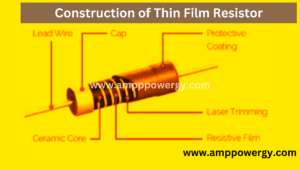
Construction of Thin Film Resistor
Thin film resistors are constructed through the sputtering processes of the resistive materials on the ceramic. After that etching techniques are required. In etching technique, the surface is etched with the ultraviolet exposer. Ater that the etched film is trimmed by laser. This resistor is made from the different materials like bismuth Ruthanne, tantalum nitride, lead oxide, nickel chromium and ruthenium oxide.
The resistance is decided by the film width which is adjusted by laser trimming. They can be sputtered to cylindrical shape by axial leads and the resulting components is called metal film resistor.
What is the Properties of thin film resistor
The following is the properties of the thin film resistor.
- The resistance value of the thin film resistor is from 0.2 – 20 Ω
- The tolerance range is from ± 0.2 to ± 2%
- Temperature coefficient is from ±5 to ±50 ppm/C°
- maximum operating temperature range is 500 C°
- And maximum operating voltage range is 50 to 500V.
- Its non-linearity is > 110 db.
- The noise of the current is 0.1 µV/V.
- Power rating is 1/16 to 1 W.
- Stability range is ± 0.15 to ± 0.5 ΔR/R.
- Its frequency behavior is high.
Thin film resistor vs thick film resistor
The thick and thin film resistor are described on the base of resistive layer used in it or on ceramic substrate used in it. The main difference between these two resistors is its fabrication processes and properties. The name of these resistor defines the thickness and thinness of the layer used in it.
Comparision of Thin film and Thick Film resistor:
| what is thin film resistor? | what is thick film resistor? |
| The resistive layer used in it is thin. | The resistive layer used in it is thick. |
| Its resistive layer thickness is 0.1 µm. | Its resistive layer thickness is thousand time high then thin film resistor. |
| metallic film is used in thin resistor which is placed on insulating substrate. | These resistors are made through firing a particular paste which is a mixer of metal oxide and glass. |
| Its temperature coefficient is low. | Its temperature coefficient is high. |
| this resistor has lower tolerance. | Thick film resistor has high tolerance. |
| The capacitance of this type of resistor is low. | The capacitance of this type of resistor is high. |
| its production cost Is high. | Tits production cost Is low. |
Characteristics of thin film resistor
In the characteristic of the thin film resistor include rated voltage, rated power, maximum element voltage, operating temperature range and power derating curve.
Rated voltage of Thin Film Resistor
The maximum rated voltage which is used in the ambient temperature is given by.
E=√R×P
HERE
“E” is the rated voltage which is measured in volts.
“R” is the resistance measured in ohm.
“P” is rated power which is measured in watts.
‘E’ represents rated which is voltage measured in volts.
‘R’ is resistance measured in ohms.
‘P’ is rated power measured in watts.
If “E” is larger than the maximum element voltage, the this the rated voltage.
Rated power of Thin Film Resistor
The rated power is the maximum power which is used continuously in the ambient temperature. The changes comes when the size changed. For heat dissipation the wide terminals and log sides are preferable, it can handle maximum power.
Maximum element voltage of thin film resistor
The maximum element voltage are the maximum AC and DC voltage applied continuously to the thin film resistor.
Operating temperature range of thin film resistor
The temperature range is where the thin film resistor is used constantly which is define the lowest and highest operating temperature.
What is Power deratings curve
The derating curve show the rang of working temperature and high power at a single point of temperature. It is also known as the current carrying curve or power rating curve.
Thin film resistor color code
the color codes are same for all resistors. the color bands are used in resistor to show the resistance value, tolerance, the temperature coefficient of the resistor.
the number of bands in the resistor can vary from 3 to 6, but most commonly used is 4 and 5 band resistors.
| colors | 1st Band of resistor | 2nd band of resistor | 3rd band of resistor | 4th band of resistor | 5th band of resistor |
| Black color | “0” | 0 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| Brown color | “1 “ | 1 | 1 | ±1% | ±1% |
| Red color | 2 | 2 | 2 | ±2% | ±2% |
| orange color | 3 | 3 | 3 | N/A | ±0.05% |
| Yellow color | 4 | 4 | 4 | N/A | ±0.02% |
| Green color | 5 | 5 | 5 | ±0.5% | ±0.5% |
| Blue color | 6 | 6 | 6 | ±0.25% | ±0.25% |
| violet color | 7 | 7 | 7 | ±0.1% | ±0.1% |
| Gray color | 8 | 8 | 8 | ±0.05% | N/A |
| White color | 9 | 9 | 9 | N/A | N/A |
The first two band represent the significant digits of the resistive value. the third band represent the multiplier (number of zeros). the fourth band represent the tolerance and the fifth band is used for temperature coefficient.
Stability and reliability of Ti/Tin as thin film resistor
The thermal stability and reliability of Ti/Tin (Ti is Titanium and Tin is titanium nitride) as a thin film resistor show that the thermal stability of Ti/Tin is 350C°. As compared to Tin (titanium nitride) layer the Ti (titanium) layer have low resistance. The breakdown mechanism of the resistor is done by joule heating.
1.3 eV thermal energy is required to break the Ti layer and 1.8eV of energy is required to break the Tin layer. According to this Ti/Tin thin film resistor are more stable for minimum for 10 years when the temperature is kept constant up to 311C°.
Titanium and Titanium nitride is used as glue layer in silicon microelectronic technologies and diffusion barriers. these films are helpful in fabrication of this resistor for RFIC (radio frequency integrated circuit) and MMICs (monolithic microwave integrated circuits). The thin film resistor parameters are TCR (temperature coefficient of resistance),Thermal stability, reliability performance and specific resistivity.
Engineers have studied tantalum and titanium nitride and proved that both are potential resistors. Few investigation about the reliability of these resistor which is utilized in the semiconductor circuits.
Advantage of thin film resistor
Advantage of the thin film resistor are the following.
- It has less temperature coefficients, and its tolerance is also low.
- There capacitance and parasitic inductance is low and less noisy.
- Its electrical performance is high
- Its power rating is high.
Disadvantages of thin film resistor
- These resistors are delicate.
- Its cost is high.
- These resistors are needed to handle carefully.
Application of thin film resistor
- These resistors are used when high accuracy, low noise and high stability are required.
- These resistors are used in electrical equipment like, measurements, testing, medical, monitoring, instrumentation, precisions audio equipment.
- These resistors are used to control op-amps gain.
- These resistors are used I voltage division, stable reference, ADC, DAC and stable feedback loops,
- These resistors are used in high accuracy measuring like measuring in aerospace, computer chips, RF application, telecommunication, power supply converters etc.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQs
Q1: What is a resistor?
Ans: resistor is two terminal devices, and it is used to limit the flow of current in electronic circuits.
Q2: what are the types of resistors?
Ans: the four main types of resistors are:
- fixed resistors.
- variable resistors.
- linear resistors.
- non-linear resistors.
Q3: what is thin film resistor?
Ans: thin film resistor is known as thin film because a thin layer of resistance is placed on the ceramic base, or core.
Q4: what is thick film resistor?
Ans: thick film resistor is called thick film because a thick layer of resistance is placed on ceramic base or core.

2 thoughts on “What are Thin Film Resistor, its Types, Application, Advantage and Disadvantage”