What is a Current dividerrule?
This article is about current and voltage divider rule.
What is Mean by an Electric Current?
Electric current is the flow of charge particles, that as electrons or holes, these charge particles are moving through a space or electrical conductor such as electrical wires. It is defined as the rate at which electrical charge flows through a surface. The particles that move through the surface are charge carriers. Which may be different type of particles, it depends on the conductor type.
In electric circuit the charge carriers are electrons which move through a wire
In semiconductors the charge carriers are electron or holes
In electrolyte the carriers are ions
In plasma there is an ionized gas, so the charge carriers are ions and electrons
Its SI unit is ampere or amp, the flow of electric charge through a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured on an ammeter or ampere meter.
Electric current creates magnetic field when it moves through winding which is used in motors, generators, transformers, inductors. Electric currents are used in telecommunication to broadcast the information which is done through the time varying current. It causes joule heating which produces light which is used in incandescent light bulbs.
The symbol of current is I ‘
What is a current DividerRule?
The current divider rule is applied when we want to find current in each Branch. It defines as a linear circuit which produces an output current that will be the friction of its input current. The current divider rule usually comes in work when the components in the circuit are connected in parallel. The is the total energy expended minimum in the circuit or the supply energy split in a parallel path in the circuit.
According to the current divider rule, the division of current in two parallel paths is inversely proportional to their resistance.
General formula for current diver rule is:
Main Article: Current and Voltage | current vs voltage | ohm law – Amppowerg
Where IT is the total current entering to the Netwerk of RX which is in parallel with RT. RT is the equivalent resistance.
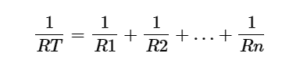
General case of Impedance in current divider rule
ZT is the total Impedance
General case For Admittance
General formula for Admittance is:
 RC combination for Current divider rule
RC combination for Current divider rule
The figure shows a simple circuit of RC combination. The capacitor and resistor are connected in parallel combination.
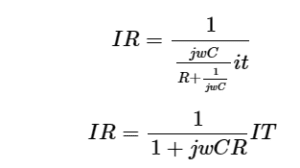 ZC =1/(jwC) is the impedance of capacitor and j is the imaginary unit.
ZC =1/(jwC) is the impedance of capacitor and j is the imaginary unit.
The product T=CR is called time constant of the circuit, and the frequency for which wCR =1 is known is corner frequency.
Capacitor has zero impedance value for high frequency and infinite for low impedance value
Example
Assume two resistor are 20 ohm and 10 ohm are connected parallel. And the current source is 20 ampere. Find current in each resistor.
DATA R1= 20 ohm, R2 =10 ohm, total current= 20A
Current across resistor R1
current across R2
Application of current divider rule
It is used to find individual Branch current when the total current and resistance is known. Current divider rule is used in different application which includes:
- It is used in the designing of electrical circuits; it is necessary to divide current in different components.
- It is used in digital logic gates, signal processing and power distribution.
- It is used in analog electronics. It is very helpful in the distribution of current in different components.
- It is also used in measuring instruments, where it helps to find high current value.
Where to use current divider rule
- You can use the current divider rule, when two or more elements are connected in parallel in a circuit with voltage or current source.
- You can use the current divider rule to find individual Branche current if total resistance and voltage are known.
- If two resistors are connected parallel in a circuit then the current in any Branche will be equal to the fraction of total current, if both resistors have equal value, then the current will divide equally in two branches.
- If three or more than three resistors are connected parallel in a circuit the total resistance is used to divide the current in all branches of the circuit.
What is a Voltage divider rule
What is Mean by a Voltage?
Voltage is also called electric potential, electric pressure or tension. Voltage is the difference between two points. It is defined as a work need per unit of charge to move a test charge or charge between two points.
SI (system international) unit of voltage is “V”.
What is Voltage a Divider Rule
The voltage divider rule is used to solve the circuit to simplify the solution. A voltage divider is a passive circuit which produces output voltage which is the friction of its input voltage. Voltage division comes in the result of distributing the input voltage among all the component.
 Voltage Divider Rule In case of electrical impedance
Voltage Divider Rule In case of electrical impedance
in the case of impedance, the voltage drops are occurred in inductors which are connecting in series. The input voltage is applied across Z1 and Z2 and the output is across Z2. the best example is auto transformer where the taping is separated.
the impedance is measured by impedance reactance.
impedance reactance formula:
XL=1/2PIfL
Voltage Divider Rule in case of low pass Filter
Consider the circuit consist of resistor and capacitor.

 Voltage Divider Rule In case of inductive
Voltage Divider Rule In case of inductive
Voltage Divider Rule In case of capacitive circuit
in capacitive voltage dividers voltage drops across the capacitor which is used to reduce high voltage value to the lower one to become easier in solving. usually, these circuits are used in touch screens like tablets, mobile phones and display devices. its work on sinusoidal AC supply and the voltage division are calculated among the capacitors with help of capacitance reactance.
capacitive reactance formula is
1/2pifC
Application of voltage divider rule:
Voltage divider rule is used to solve and simplify electrical circuits. It reduces the amplitude of voltage or it create reference voltage.
Applications of voltage divider rule
here are some applications of voltage divider rule.
- Usage in biasing circuit in BJT amplifier: it is used to set the Biase voltage for transistor in the amplifier circuits.
- Feedback circuits: it is used to give feedback in the operational amplifier circuit.
- Comparator circuits: it is used in comparator circuit for comparing various voltage.
- Voltage regulation: it is used to regulate voltage in a circuit.
- Potentiometer: it is used for varying the resistance in potentiometers to control the output voltage.
- Adjusting signal levels: it is used for adjusting signal levels in a circuit.
- Biase of active device: it is used in Biase of active device in amplifier circuits. It sets Biase voltage for active devices.
Voltage Divider Rule used in Sensor measurement
voltage divider is used to measure the value of sensor by allowing the microcontroller. the wired in series with a known resistor to for voltage divider and the known voltage value is applied across the voltage divider. the microcontroller is connecting to the center tapped so that it can measure the value of voltage and by using this voltage the sensor is resistance is computing.
Voltage Divider Rule used in High voltage measurement.
voltage divider is also used to reduce the high voltage to low voltage for measure the voltage on meter. the high voltage is applied to the divider and the output of the divider is become low. so the meter is then capable to take the reading.
Voltage Divider Rule used in Level of shifting.
the voltage divider is also use as a level shifter of digital circuit.
Example on Voltage Divider Rule
Example:
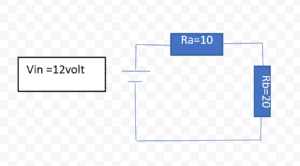
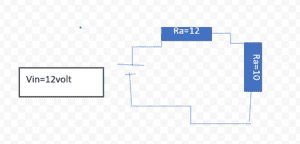
Determine the output voltage of the circuit with the resistor Ra and Rb is 10 ohm and 12ohm with the output voltage is 12 volts.
Ra = 10 ohm, Rb = 20
and applied voltage is 12 volts.
Solution:
Voltage divider formula is.
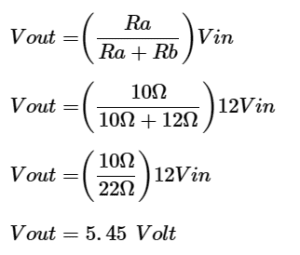 Example
Example
Determine the input voltage of voltage divider circuit whose resistor value is. R1=20 Ω and R2 = 30 Ω and the output voltage is 12v.
Ra=12 ohm, Rb=10 ohm
applied voltage is 12 volt
Voltage divider formula is:
Frequently asked Question FAQs
Q1: what is electrical current?
Ans: moving of electrical charges in a circuit is called electrical current.
Q2: what is the unit of electrical current?
Ans: the SI unit of electrical current is ampere which is denoted by “A”.
Q3: what is the main two type of electrical current?
Ans: the main two type of electrical current is:
- Alternating current
- direct current
Q4: what is the properties of electrical current?
Ans: the properties of electric current includes heating effect and magnetic effect.
Q5: what is voltage?
Ans: voltage is also called electrical potential. it is a force which drive electrical current in a circuit.
Q6: what is the unit of voltage?
Ans: the SI unit of voltage is volt which is denoted by “V’.
Q8: what instrument is used to measure electrical current?
Ans: ammeter and ampere meter are used to measure electrical current.
Q9: what instrument is used to measure electrical voltage?
Ans: electrical voltage can be measured by the instrument called voltmeter or DMM (digital multimeter).
Watch video on current divider rule: Bing Videos
Watch video on voltage divider rule: Bing Videos
More Articles
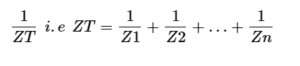
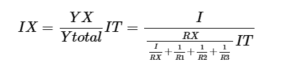
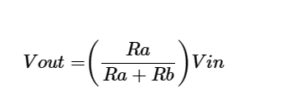
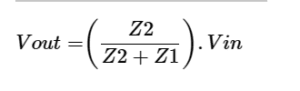
4 thoughts on “What is a Current Divider Rule and What is Voltage Divider Rule”