Current and voltage or current vs voltage
Overview of Electrical current and voltage
If we turn the knob or push the button we have instant power, it is due to current and it is possible due to voltage because it is voltage which pushes current.
What is Mean by Electric Current
Current Is the rate it which electric charge flows through a space or electric circuit.
The flow of charge particles is current. In metals the charge particles is free electron.
In gases current flow in the form of ions. The positive ion flow in one direction and the negative ion flow in the opposite direction.
Current is measured in ampere, but we can write only “A” and denoted by “I”.
The rate of flow of electron in a conductor is called current.
Electron is a very small particle which exists in the molecular structure of a substance. Sometime electrons are tightly bounded, and sometime electrons are loosely bounded. The electrons which are loosely bound can move freely in the body of conductor. Electrons are negative particles when they move, it means charges are moved and this movement of electron is called electrical current. It is an electron which brings the ability to the conductor to conduct electricity. There are some materials in which electrons can move better than the others, due to this property materials are classified into conductor and insulator.
What is Mean by an Electrical conductor?
Conductors are the materials which allow the charges to move freely its body. It allows the electron to move from body to another. The movement of electron inside the conductor creates current and the force which is required to move the charges in the conductor is called voltage.
Example of conductor
Human body, solution of salt, and metals such as iron, silver and gold.
Note:
Silver is a good conductor.
What is insulator:
Insulators are materials which do not allow charge particles to move freely. It restricts electrons from moving from one body to another.
Example of insulator:
The following are the best example of insulator.
- Plastic
- Wood
- Glass
.Electrical circuits need energy sources like batteries which produce voltage. Without voltage electron flow randomly and undirected. Voltage moves electrons in one direction. An electrical circuit is a closed loop in which electron flow in one direction.
What is mean by an electromotive force (emf)?
Electrons are flowing undirected in electrical circuit when no force is applied on them. Now to make them in a particular direction some extra force is required. The force which acts on the electron to give them a single direction is called electromotive force. It is also called voltage which is measured in volts.
What is the Unit of an electric current
Electric current is measured in ampere which is denoted by a latter A. ampere is defined as one Columb charge flow in per second.
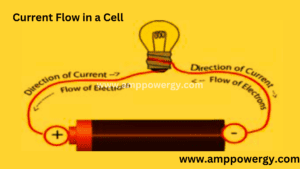
What is Conventional current flow vs electron flow
A lot of confusion is there in conventional current flow and electron flow lets solve this confusion.
Conventional current flow
It is a flow of electric current from positive to the negative terminal and its direction is toward positive charges.
Electron flow
It is a flow from negative to positive terminal. Electrons are negative charge particles so positive charge attracts negative charges.
Properties of an electric current
- Work is done in moving of electron in electrical conductor, this work sone is called electrical energy. Electrical energy ca be converted to other forms which include heat energy and light energy.
- There is ae two types of electric current, which includes DC and AC. Direct current can move only in one direction, and it is mostly used in low voltage applications, alternating current can move in two directions, and it is used in high voltage applications.
- There are two directing of electrical current which is conventional direction and electron direction. Conventional direction is from positive to negative, and electron direction is from negative to positive.
What are the Effects of an electric current
Heating effect of an electrical current
when current flows through a conductor heat is produced like an iron box.
Equation for heating effect
Heating effect depend upon the following points which is.
- Time (t): longer the time in which current flow in a conductor move heat will produce.
- Electrical resistance: the higher the resistance, the higher will be the.
- Amount of current: the higher the current, the higher will be the heat. The lower the current, the lower will be the heat which will not be noticed.
Magnetic effect of an electrical current
When electric current flows in conductor it produces magnetic field. When compass is place near the conducting wire which carries electric current. When the needle of the compass deflect it means magnetic field produced.
Chemical effect of an electrical current
When electric current passes through a solution, the solution gets ionized and breaks into ions because chemical reaction occurs in it. When electric current passes through a solution the following effects can occur.
- It can change the color of the solution.
- It can create a metallic deposit on the electrode of the conductor.
- It can release gas.
- It can produce bubbles in the solution.
Read Main Article About current
What is Mean by an electricalVoltage?
The popular definition of “voltage is the total work or force needed to move a charge on between two points”. Voltage is also called potential difference or electric pressure.
As per definition voltage is the difference in the electrical potential between two points or it is a work needed to move a charge from one place to another place.
voltage is a force which drives the electric current in a circuit. Voltage is known by electric pressure, electric tension, Voltage is measured in volts and denoted by “V”.
Comparison of an Electrical current and voltage
| electrical Current (I) | electrical Voltage (V) | |
| Symbol | “I” | “V” |
| Definition | electrical Current Is the rate it which electric charge flows in a space or electric circuit. Current is measured in ampere and denoted by “I”. | Voltage: voltage is a force which is responsible to drives current in a electrical circuit. Voltage is measured in volts which is denoted by “V”. |
| Unit | Ampere (A) | Voltage(V) |
| Measuring Instrument | Ammeter, clamp meter Ampere meter | Voltmeter, galvanometer |
| SI Unit | 1 Ampere=1 Coulomb/Second. | 1 Volt = 1 Joule/Coulomb. |
| Field created | A magnetic field | an electrostatic field |
| In series connection | Current remains same when the component is connected in series | Voltage is not remained same when the component is connected in series I.e voltage get divided in series connection |
| In a parallel connection | Current is not the same in parallel connection. I.e. current get divided in series connection | Voltage is same in parallel connection. |
What is the Relationship Between Electrical Voltage and Current
Voltage and current both are very essential properties in electricity. Current cannot move by itself in electrical circuit, cables, wires this is voltage which is responsible to move electrical current in circuits.
Voltage is the potential difference between two points. It is also called electromotive force (EMF).
This force is actually moving the free electron I.e. current in circuit.
Voltage and current can flow in a closed loop if the loop is not completed the current and voltage cannot move. So close loops are very important for the flow of electricity.
Symbols and Units of Electrical Current and Voltage
Symbol “I”
Unit “ampere”
SI unit “coulomb/ second”
1 ampere = 1 coulomb/second.
I Columb = 6.24 * 10 18
One ampere of current can one coulomb charge in a circuit
Electrical Voltage
Symbol “V”
Unit “volt”
SI unit “joule/coulomb”
One volt drives one coulomb of charge through a resistance of one ohm
Ohm is the unit of resistance
Measuring instrument “voltmeter”
Field and intensity of an Electrical current and voltage
Electrical Current produce magnetic field. Stronger the current, stronger the magnetic field
Electrical Voltage produces electrostatic field as the distance increases between the two points the electrostatic field decreases.
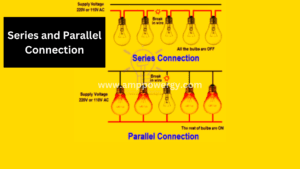
Current and Voltage in Series and parallel connection
In Series connection
In series connection the current remains same while the voltage gets divided.
In Parallel Connection
In parallel connection the voltage remains same while the current gets divided
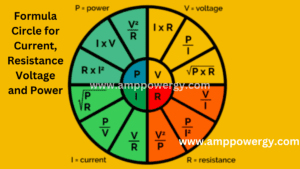
Importance of Ohm law in current and voltage
Ohm law tells us that the voltage across the conductor is directly proportion to the current and voltage.
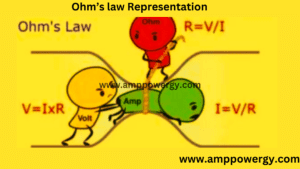
Mathematically representation of ohm law
V=IR equation 1
If current and resistance is known, we can find the voltage by equation 1
I=V/R equation 2
If voltage and resistance is known, we can find current by equation 2
R=V/I equation 3
If voltage and current is known, we can find resistance by equation 3
Frequently Asked Question FAQS
Q; Why is cooper wire preferred?
Ans: Because copper wire offers low resistance for the flow of current.
Q: What will happen if voltage is missing in a circuit?
Ans: If voltage is missing in a circuit there will be no flow of electricity.
Q: what is the unit of current?
Ans: the unit of current is ampere.
Q: what is the unit of voltage?
Ans: the unit of voltage is volt.
Q: what is electrometer?
Ans: electrometer is an instrument designed to measure very small current and voltage.
Q: why is copper used in connecting wires?
Ans it is because the resistivity of copper is very low.
Q: what is the reciprocal of resistance?
Ans the reciprocal of resistance is conductance.
Q: what happens to the resistance of pure metal and semiconductors when temperature increases?
Ans: the resistance of metal increases when temperature increases while the resistance of semiconductors decreases when temperature increases.
Q: what is an insulator?
Ans: insulator is the material which does not allow electrons to move freely.
Q: what is electric charge?
Ans: it is a property of subatomic particles which experience force when placed in the electric or magnetic field.
Q: how to measure absolute resistance?
Ans: to measure the absolute resistance a method is used called Wheatstone bridge method.
Q: what is electromotive force (emf)?
Ans: electromotive force or emf is an electrical potential which is produced by electromechanical cells or changing magnetic field.
Q: what happens to the power when voltage increases?
Ans: due to formula when voltage increase power will also be increase. Because electrical power is the multiplication of current and voltage
Q: what happens to the current when voltage increases?
Ans: due to ohm law when voltage increase current will also be increase.
Informative article